ABOUT IT!
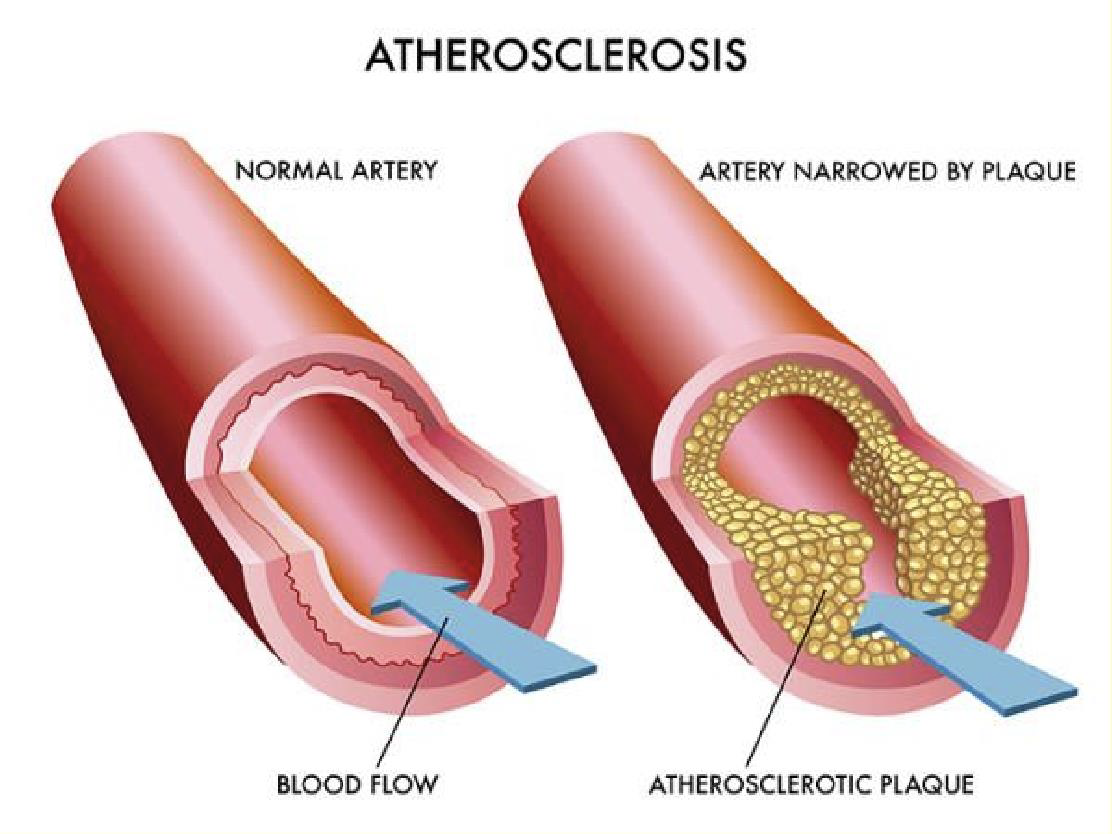
Arteriosclerosis: When the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients become thickened and stiff. This condition will reduce the blood flow to the organs and tissues. Healthy arteries are flexible and elastic.
Atherosclerosis: Build-up of fats, cholesterol within the artery walls forming a lump that narrows the arteries called plaque. This plaque deposits are what causes arteries to narrow and blocks the blood flow. At times these plaques that burst within the arteries causing blood clots which have high risks of breaking apart, travelling and clogging arteries of other vital organs causing a heart attack (Heart arteries are clogged) or a stroke (Brain arteries are clogged). Healthy lifestyle habit can help prevent atherosclerosis.
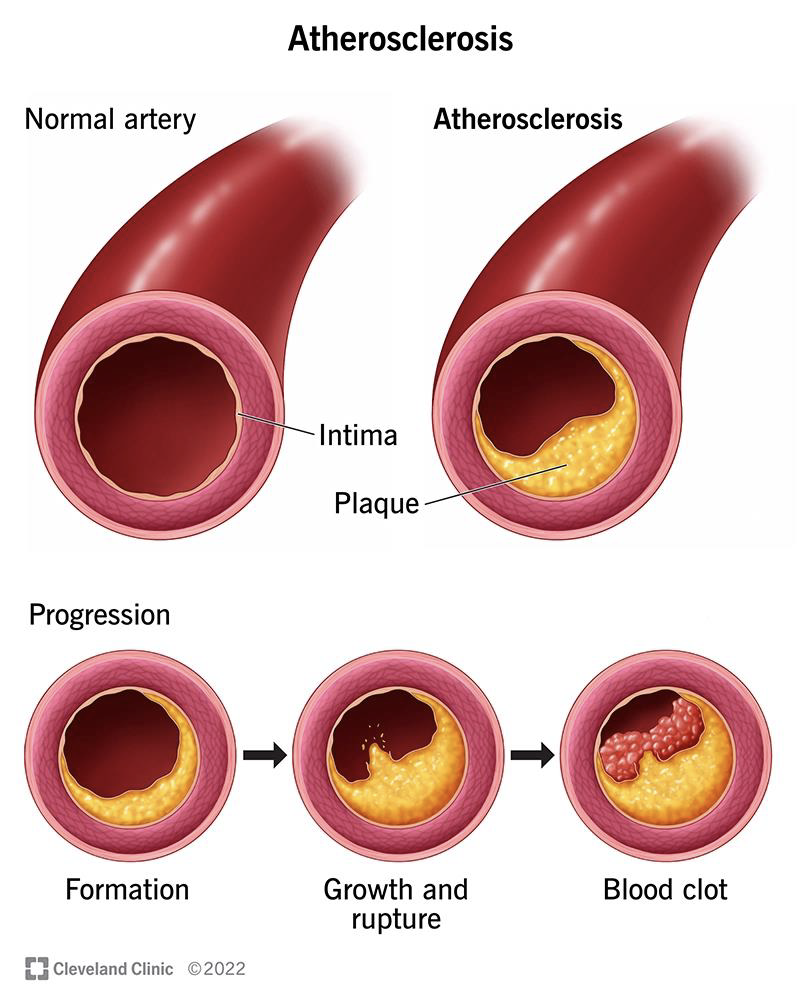 Development of Atherosclerosis
The exact cause of the development of atherosclerosis is unknown but the damage usually starts sue to injuries that occur within the inner layers of your arteries. Once the inner wall of an artery is damaged, blood cells and other substances (Cholesterol / fat deposits) may gather at the injury site and build up in the inner lining of the artery. These damages are usually due to:
Development of Atherosclerosis
The exact cause of the development of atherosclerosis is unknown but the damage usually starts sue to injuries that occur within the inner layers of your arteries. Once the inner wall of an artery is damaged, blood cells and other substances (Cholesterol / fat deposits) may gather at the injury site and build up in the inner lining of the artery. These damages are usually due to:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- High triglycerides (A type of fat (lipid) in the blood)
- Smoking / Chewing on Tobacco
- Diabetes
- Insulin resistance
- Obesity
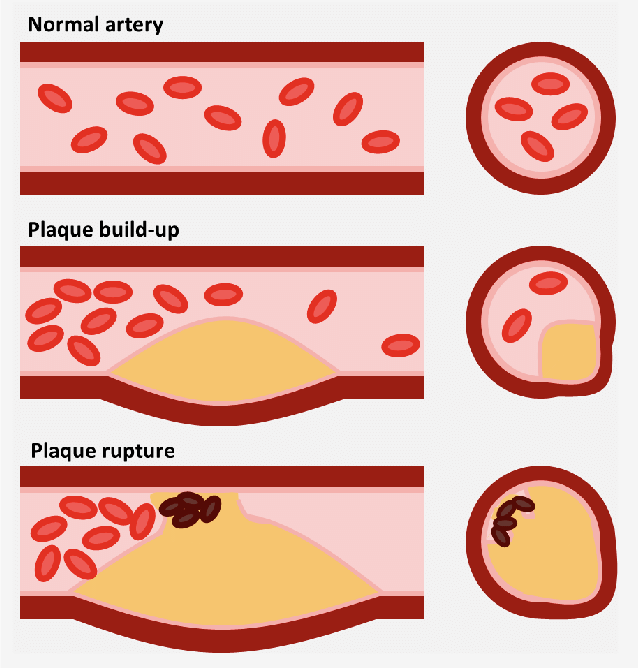 Know the Risks of Developing This!
Know the Risks of Developing This!
- Aging (Old Age)
- Smoking
- Consuming an unhealthy diet (High in Fats, Salt, Sugar)
- High Cholesterol
- Obesity
- Family history of heart diseases
- Pre-Existing Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Physical Activity
- Sleep apnoea
- Do you experience any chest Pain during / after physical activity?
- Do you experience any chest Pain during rest?
- Do you have shortness of breath after climbing a flight of stairs?
- Do you have shortness of breath after / during physical activity? (Walking a short distance), Does it worsen by day?
- Do you experience any sudden numbness or weakness in your arms/legs?
- Any temporary loss of vision in one eye?
- Are you experiencing any slurred speech?
- Do you notice any drooping in the muscles of your face?
Arteries within your Arms and Legs
- Do you experience leg pain when walking? (Claudication)
- Do you experience increase in severity of the pain as you walk a greater distance?
- Does the pain relieve on rest?
Arteries leading to your Kidneys
- Are you experiencing any sudden increase in your blood pressure?
- Do notice any blood or frothy urine lately?
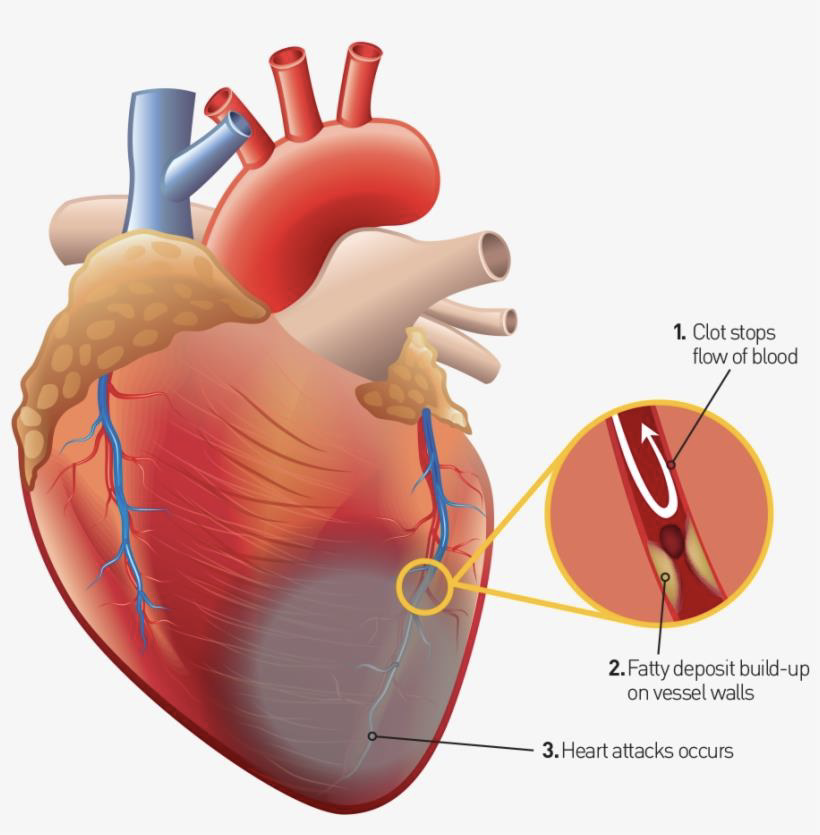 HOW DOES ARTHEROSCLEROSIS LEAD TO ORGAN DAMAGE?
The complication and severity depend on which organ’s artery is clogged and to what extent
HOW DOES ARTHEROSCLEROSIS LEAD TO ORGAN DAMAGE?
The complication and severity depend on which organ’s artery is clogged and to what extent
- Coronary Artery Disease: - When the arteries close to your heart are clogged it will cause Angina(chest pain), Heart Attack or Heart Failure.
- Carotid Artery Disease - When the arteries close to your brain are clogged this can cause Strokes or Transient Ischemic attacks (Short term).
- Peripheral Artery Disease -When the arteries in your arms or legs are clogged, this can make you less sensitive to heat and cold, increasing your risk of burns or frostbite and rarely death in organ tissues causing gangrene.
- Aneurysms. - This is a serious complication that can occur anywhere in your body. This will cause severe pain and throbbing within the affected area and if burst can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding.
- Chronic Kidney Disease. - When arteries leading to the kidneys are clogged affecting blood flow to the kidneys and reducing the ability of kidneys to filter waste and excess fluids from the body.
Some of the additional tests done during diagnosis of your condition may include:
- Laboratory Blood tests - To check blood your sugar and cholesterol levels. High levels of blood sugar and cholesterol raise the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). - This is a painless and fast procedure that measures the electrical activity of the hear which helps determine if there's reduced blood flow to your heart.
- Exercise Stress Test - Usually done if you have symptoms during physical activity. You'll walk on a treadmill while your heart is monitored. This test can show heart problems that may be missed when you are at rest and your heart is not pumping as actively. If you can't exercise, you may be given a medication that mimics the effect of exercise on your heart.
- Echocardiogram - Uses sound waves to visualize the blood flow through the heart.
- Doppler ultrasound - This is done to measure your blood pressure at various points along your arm or leg which indicated the speed of blood flow within your arteries.
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI) - This test compares the blood pressure in your ankle and your arm to check for atherosclerosis in the arteries of your legs and feet. If there is a difference is measurements then there is a high chance it is caused by atherosclerosis within those arteries.
- Cardiac Catheterization and Angiogram - This test uses a dye that flows through a catheter placed within your blood vessel. The dye that flows through the catheter to arteries of the heart will be able to show clear images of any narrowed or blocked arteries.
- Coronary Calcium Scan - This is a heart scan that uses, (CT) imaging to create detailed pictures of the heart. It can show calcium deposits in the artery walls.
- To check for C-reactive protein (CRP) that may suggest any inflammation of the arteries.
- QUIT SMOKING
- Control and Monitor your Blood Pressure - Optimal blood pressure is less than 120 systolic and 80 diastolic, as measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
- Control and Monitor your Cholesterol Levels. Screen your cholesterol levels more regularly if you have a history of high cholesterol is in your family. Aim for a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) level below 3.4 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
- If you have other risk factors for heart disease, aim for an LDL level <2.6 mmol/L
- If you're at very high risk of heart disease or you have already had a heart attack or have diabetes, aim for an LDL level <1.8 mmol/L
- Control and Monitor your Sugar levels
- Exercise - Physical activity helps you achieve and maintain a healthy weight and control diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressure —aim for 30 to 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week.
- Consume a Healthy and Balance Diet - Reduce your consumption of saturated fat, cholesterol, sodium and added sugar and increase your intake of fruits and vegetables.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight - A body mass index (BMI) of less than 25 and a waist circumference of < 88cm is the goal for preventing and treating heart disease.
- Manage stress - Reduce stress as much as possible. Practice techniques for managing stress, such as muscle relaxation and deep breathing.
It is recommended that everyone over age 20 should get their cholesterol levels measured at least once every 5 years. The test that is performed is a blood test called a lipoprotein profile. That includes:
- Total cholesterol level
- LDL (the "bad" cholesterol)
- HDL (the "good" cholesterol)
- Triglycerides
- Your Diet - Saturated fat, trans fat, carbohydrates, and cholesterol in the food you eat increase cholesterol levels. Increasing the amount of fibre and plant-derived sterols can also help lower LDL cholesterol.
- our Weight - Losing weight can help lower your LDL, total cholesterol levels, and triglyceride levels, as well as raise your HDL.
- Exercise - Regular exercise can lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. You should try to be physically active for 30-40 minutes every day.
- Age and Gender - Cholesterol levels will rise with age. Before menopause, women tend to have lower total cholesterol levels than men of the same age. After menopause, however, women's LDL levels tend to rise.
- Heredity - High blood cholesterol can run in families. Be sure to check your cholesterols levels regularly if you have a family history of cholesterol.
- Medical conditions - Certain medical condition can cause an elevation of cholesterol levels in the blood. These include hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid gland), liver disease and kidney disease.
- Eat a healthy diet (Less salt, sugar and fats)
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain a healthy weight (Your Ideal BMI)
- Go for regular screening and monitoring